Summarize data in your reports to obtain totals, averages, aggregates, and so on.
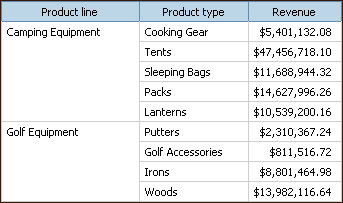
In a report, you can add both detail and summary aggregation. Detail aggregation, which is supported only for relational data sources, specifies how a data item is totaled at the lowest level in a report. In lists, detail aggregation specifies how the values that appear in the rows are totaled. In crosstabs, detail aggregation specifies how the values in the cells are totaled. For example, detail aggregation for a measure like Revenue might be Total in both lists and crosstabs. In the following list report, this means that the values you see for the Revenue column represent the total revenue for each product type.

Summary aggregation, which is supported for all data sources, specifies how data items are totaled in the headers and footers of a list and in the total rows and columns of a crosstab. For list reports, these summary aggregates only summarize the data that is visible on that page of the report.
You can specify detail and summary aggregation in different ways by using any of the following:
If a summary is applied to a report that contains binary large object (BLOB) data, such as images or multimedia objects, you cannot also perform grouping or sorting.
How data is aggregated also depends on the type of data that you are aggregating. Aggregation rules are applied differently to facts, identifiers, and attributes. For example, if you aggregate a data item that represents part numbers, the only aggregate rules that apply are count, count distinct, count non-zero, maximum, and minimum. For information about how to determine the type of data that a data item represents, see Add Relational Data to a Report and Add Dimensional Data to a Report.
You can add simple summaries to the groups in a report
by using the aggregate button. This button provides a subset of
the aggregate functions available in Report Studio. For list reports,
a Custom option is also available so that you
can add your own aggregate function in the expression of the data
item  .
.
The aggregate button sets the rollup aggregate property  for
the data item to the selected summary aggregate, and places the
data item into an appropriate footer. A footer is created for each
group as well as an overall footer, unless they already exist.
for
the data item to the selected summary aggregate, and places the
data item into an appropriate footer. A footer is created for each
group as well as an overall footer, unless they already exist.
For information about adding a rolling or moving average, see Rolling and Moving Averages.
Click the column to which to add a summary.
To change the summary label, do the following:
Click the label.
In the Properties pane, under Text Source, set the Source Type property to the source type to define the label.
For example, set it as Data Item Value to produce a dynamic label for the summary based on data item values.
Set the property below Source Type to specify the label.
This property depends on the source type you chose. For example, if you chose Data Item Value as the source type, set the Data Item Value property to the data item to use to define the label.
In lists, the summary appears as a footer  .
If the column to which you added a summary is grouped, group and
overall summaries appear. In crosstabs and charts, the summary appears
as a node
.
If the column to which you added a summary is grouped, group and
overall summaries appear. In crosstabs and charts, the summary appears
as a node  .
.
To change a summary, select it and,
in the Properties pane, under Data
Item, click Rollup Aggregate Function and
choose a different function.
and
choose a different function.
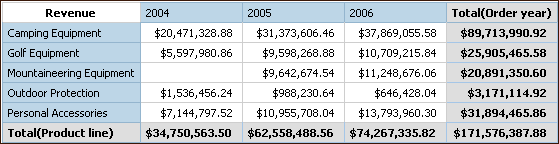
In crosstabs, you can add multiple summaries at the same level. For example, you have a crosstab with Product line as rows, Order year as columns, and Revenue as the measure. For Product line, you can add the Total summary as a header, which will total all revenue for each order year. You can then add the Average summary as a footer, which will give the average revenue of all product lines for each order year.
Set the Auto Group & Summarize query property to specify whether Report Studio should group non-fact data items (identifiers and attributes) and apply aggregate functions to aggregate fact data items in lists.
If you are using an OLAP data source, data is always summarized regardless of how this property is set.
Pause the pointer over the query explorer button  and
click a query.
and
click a query.
In the Properties pane, set the Auto Group & Summarize property:
To group non-aggregate fact data items and apply aggregate functions to aggregate fact data items in lists, set this property to Yes.
To render detail rows, set this property to No.
When working with relational or dimensionally-modeled relational (DMR) data sources, you can use the aggregation properties specified for the query item in the Framework Manager model instead of specifying detail or summary aggregation in the report. The model specifies the default summary function for each query item.
Aggregation functions are mapped between data sources, Framework
Manager, and Report Studio  .
.
When working with relational data sources and list reports,
for each data item in a report, you can specify detail and summary
aggregation properties to manage summaries without having to create
complex data item expressions  .
.
Click the data item for which to set detail or summary aggregation.
In the Properties pane, set the Aggregate
Function or the Rollup Aggregate Function property
to a function  .
.
You can use summary functions in data item expressions.
The summary functions in the Expression Editor  that
have the same name as the summary functions available through the Aggregate
Function and Rollup Aggregate Function properties
that
have the same name as the summary functions available through the Aggregate
Function and Rollup Aggregate Function properties  operate
the same way. For example, in a relational report, setting the Aggregate
Function property to Total is the
same as changing the expression of the data item to total([Revenue]).
operate
the same way. For example, in a relational report, setting the Aggregate
Function property to Total is the
same as changing the expression of the data item to total([Revenue]).
In general, report maintenance is easier if the Aggregate Function and Rollup Aggregate Function properties are used rather than adding aggregate functions to data item expressions. Use summary functions in expressions if the required summary is not supported as an aggregate or rollup aggregate property or if the complexity of the expression cannot be managed using the data item properties. Add an aggregate function to a data item expression if one of the following conditions applies:
The underlying data source is relational, and you want to use database vendor-specific aggregate functions.
You want to use aggregate functions that require more than one parameter, such as percentile.
You require aggregate expressions that are not available in the aggregation properties, such as a for clause.
For example, your report uses Product line, Product type, and Quantity. You want to calculate the percentage of the parent quantity that is represented by each product type. This requires you to compare the total quantity for each product type to the total quantity for the parent product line. In other words, your expression requires aggregates at different group levels. You use aggregate functions in the data item expression with a for clause to specify the group level as follows:
total ([Quantity] for [Product type]) / total([Quantity] for [Product type])
Tip: The Total Revenue by Country sample report  in
the GO Data Warehouse (query) package includes a total aggregate
function. For more information about The Great Outdoors Company
samples, see Sample Reports and Packages.
in
the GO Data Warehouse (query) package includes a total aggregate
function. For more information about The Great Outdoors Company
samples, see Sample Reports and Packages.
Click a data item.
In the Properties pane, double-click the Expression property and add aggregate functions to the expression for the data item.
A summary function that uses a for clause may yield unexpected results. These may include error messages, warnings, incorrect numbers, and more or fewer than expected rows, columns, or chart points and lines.
To avoid these problems, ensure that the parameters that follow the for clause adhere to the following constraints:
Parameters must be simple data item references.
All data items in the parameter list must appear on every list, crosstab, or chart that uses that summary.
For any edge used in the for clause, data items listed in the for clause must start with the first data item on that edge.
Data items must be listed in the order in which they appear on each edge of the report with no gaps.
In crosstabs and charts, there must be no sibling data items that are considered details. Summaries are normally not considered details.
Section headers must not be included in the parameter list.
If following these constraints does not resolve the problems and your report uses dimensional data with no detail or summary filters, consider using the within set clause instead of the for clause.
This section describes the summary functions that are
available in Report Studio. Some functions, such as Custom, are
available only when you click the aggregate button  on
the toolbar. Additional summary functions are available in the Expression
Editor
on
the toolbar. Additional summary functions are available in the Expression
Editor  .
.
In lists, sets the summary function to Automatic.
In crosstabs, sets the Rollup Aggregate Function to Automatic.
The Aggregate function  uses the summary rules
for Automatic.
uses the summary rules
for Automatic.
Depending on the type of data item, applies the function None, Summarize, or Calculated based on the context in which the data item appears.
Calculated is applied if the underlying data source is OLAP. It is also applied if the data item expression
contains a summary function
is an if-then-else or case expression that contains a reference to at least a modeled measure in its condition
contains a reference to a model calculation or to a measure that has the Regular Aggregate property set to a value other than Unsupported
contains a reference to at least one data item that has the Rollup Aggregate Function property set to a value other than None
If the underlying data source is relational and if the data item expression contains no summary functions and a reference to at least one fact that has the Regular Aggregate property set to a value other than Unsupported, Summarize is applied.
If the underlying data source is OLAP and if the data item expression contains no summary functions and a reference to at least one fact that has the Regular Aggregate property set to a value other than Unsupported, Calculated is applied.
If the underlying data source is SAP BW, reports containing aggregations and summaries run more efficiently if the aggregation applied to a query item matches the aggregation rule for the underlying key figure on the SAP BW server. In Report Studio, the easiest way to accomplish this is to change the value of the Aggregate Function property to Automatic.
In all other contexts, None is applied.
For relational and dimensionally modeled relational (DMR) data sources, if this function is applied to a data item expression that has the average function, weighted averages are computed based on the lowest level detail values in the data source.
This is the default function.
Adds all existing values and then divides by the count of existing values.
Specifies that all the terms within the expression for a data item are aggregated according to their own rollup rules, and then the results of those aggregations are computed within the overall expression.
For example, a list contains the data item Quantity with the Aggregation property set to Total. You add a query calculation named Quantity Calculated. You define its expression as Quantity + 100 and you set its Aggregation property to Calculated. When you run the report, the values for Quantity Calculated are computed by first adding all values for Quantity and then adding 100 to each value.
In crosstabs, this function overrides any solve orders that
are specified  .
.
Counts all existing values.
If the underlying data source is OLAP, Count behaves as follows if it is specified in the Rollup Aggregate Function property for a data item.
Object | Behavior |
Level | Count distinct is used. A warning appears when you validate the report. |
Member set | Count distinct is used. A warning appears when you validate the report. |
Attribute | Not supported. An error is returned when you run the report. |
Measure | Supported. |
If the underlying data source is dimensionally modeled relational (DMR), Count behaves as follows if it is specified in the Aggregate Function or Rollup Aggregate Function property for a data item.
Object | Behavior |
Level | Count distinct is used. A warning appears when you validate the report. |
Member set | Count distinct is used. A warning appears when you validate the report. |
Attribute | Supported. |
Measure | Supported. |
If you add the Count summary to a non-fact column in a list and then group the column, the column will not be grouped when you run the report. To resolve this issue, group the column first before adding the Count summary.
Returns the total number of unique non-null records.
If the underlying data source is OLAP, Count Distinct behaves as follows if it is specified in the Rollup Aggregate Function property for a data item.
Object | Behavior |
Level | Supported. |
Member set | Supported. |
Attribute | Not supported. An error is returned when you run the report. |
Measure | Not supported. An error is returned when you run the report. |
If the underlying data source is dimensionally modeled relational (DMR), Count Distinct is supported for levels, member sets, attributes, and measures when it is specified in the Aggregate Function or Rollup Aggregate Function property for a data item.
Summarizes data based on an expression that you define.
Selects the largest existing value.
Returns the median value of the selected data item.
Selects the smallest existing value.
Does not aggregate values.
If the underlying data source is relational, the data item is
grouped when the query property Auto Group & Summarize is set to Yes.
is set to Yes.
This function is available only for the Aggregate Function property. It specifies that the aggregate attribute is ignored. For example, the calculation will be applied after the data is aggregated.
This function differs from the Calculated function, which applies aggregation to the rows and then performs the calculation.
For example, for the average([Quantity])+5 expression, when the Aggregate Function property is set to Not Applicable, five is added to the average of the single Quantity value. When the function is set to Calculated, five is added to the average of a set of numbers.
This setting should not be applied to a simple model reference.
This setting is relevant only for reports that are upgraded from IBM Cognos ReportNet® 1.x.
Returns the standard deviation of the selected data item.
From a mathematical perspective, this function is not useful
for small numbers of items and is not supported if the query property Auto
Group & Summarize is set to Yes.
is set to Yes.
Aggregates data based on model or data type information. This function can be thought of as a calculate and then aggregate rule. Data is aggregated using the following rules:
If the underlying data source type is relational and the data item or calculation is a reference to a single fact query item in the model that has the Regular Aggregate property set to Sum, Maximum, Minimum, Average, or Count, aggregate data using this function. Otherwise, data is aggregated according to the data type of the data item as follows:
Total is applied for numeric and interval values.
Maximum is applied for date, time, and date-time values.
Count is applied for everything else.
The underlying data source type can be dimensional and the data item or calculation a reference to a single item in the model. In this case, if the Regular Aggregate property of the model item is not unknown, the summary function that corresponds to the Regular Aggregate property is applied. If the Regular Aggregate property is unknown, set the function to Calculated.
For example, a list contains the data item Quantity with the Aggregation property set to Average. You add a query calculation named Quantity Summarize. You define its expression as Quantity + 100 and you set its Aggregation property to Summarize. When you run the report, the values for Quantity Summarize are computed by first adding 100 to each value for Quantity and then calculating the total. The total is calculated because Quantity contains numeric values and the expression for Quantity Summarize is not a simple data item reference. If Quantity Summarize is defined as Quantity, the function Average is applied to each value.
Adds all existing values.
Returns the variance of the selected data item.
Note: From a mathematical perspective, this function is not useful for small numbers of items and is not supported if the query property Auto Group & Summarize is set to Yes.
The summary functions available in Framework Manager and Report Studio reflect summary functions supported by relational and dimensional data sources. The following table shows how summary functions in data sources are mapped to Framework Manager and Report Studio.
Data source | Framework Manager | Report Studio |
None specified, or none | Unsupported | None |
average (avg) | Average | Average |
count | Count | Count |
count distinct | Count Distinct | Count distinct |
maximum (max) | Maximum | Maximum |
minimum (min) | Minimum | Minimum |
median | Median | Median |
standard deviation (stddev) | Standard Deviation | Standard Deviation |
sum | Sum | Total |
variance (var) | Variance | Variance |
count non zero | Count Non-Zero | Automatic |
average non zero | unknown | Automatic |
external | unknown | Automatic |
any | unknown | Automatic |
calculated | unknown | Automatic |
unknown | unknown | Automatic |
first_period | unknown | Automatic |
last_period | unknown | Automatic |
The following summary functions exist only in either Framework Manager or Report Studio. There is no corresponding summary function in data sources.
Framework Manager | Report Studio |
Automatic | Automatic |
Calculated | Calculated |
No corresponding summary function | Summarize |
No corresponding summary function | Not Applicable |
